Otoplasty, also known as ear surgery or ear pinning, is a cosmetic procedure that reshapes and repositions protruding ears and other abnormalities. The surgery contours the ears to make them less prominent, thus restoring patients with a balanced facial profile.
Our recommended plastic surgeons have extensive experience performing all types of otoplasty and other cosmetic ear procedures. They will design a bespoke surgery according to your unique features and requirements to provide a result that looks natural.
Treatments
1Results
ImmediateSurgery time
1-3 hoursHospital time
6 hoursMobility
ImmediateWashing
1 weekStay home
4 daysOff-Work
5 daysExercise
2 weeksFull recovery
4 weeksOtoplasty Before and Afters
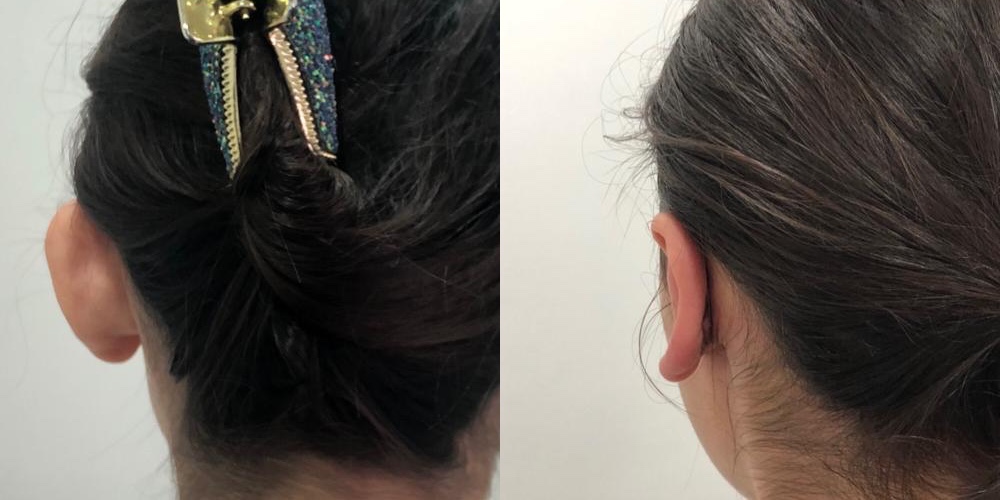
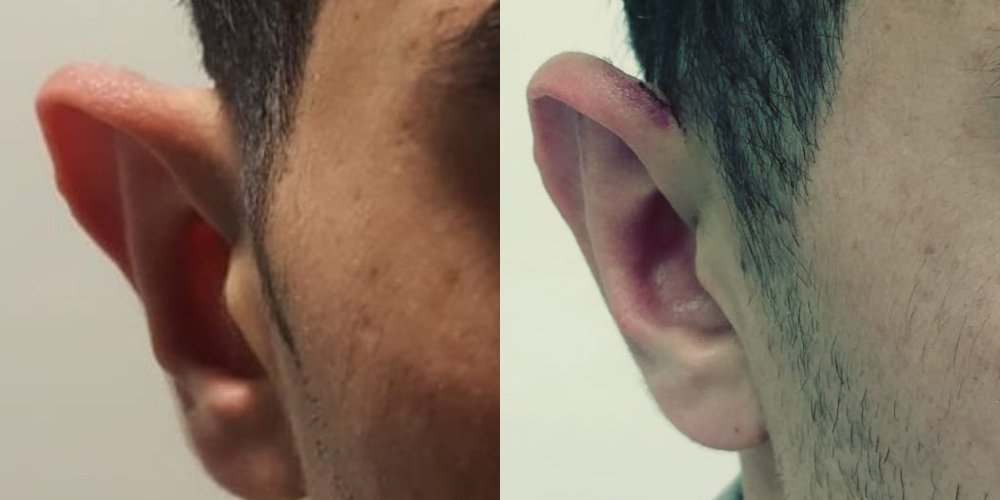
Is Otoplasty Worth it?
Protrusion and other deformities in the ears are a source of self-consciousness for many people. Therefore, many patients consider otoplasty to be a worthwhile cosmetic procedure as it creates a balanced facial profile.
Flatten Protruding Ears
If your ears are more than 2cm or 35° away from the side of the head, they may be considered protruding. In such cases, the ears become a prominent feature of the facial profile, which many people wish to correct. By reshaping the cartilage, an otoplasty flattens protruding ears and repositions them closer towards the head.
Correct Ear Abnormalities
An otoplasty corrects a range of other ear abnormalities, including asymmetrical ears, disproportionately small or huge ears, and distorted results from previous ear surgery. These abnormalities are usually the result of congenital birth deformities that can be corrected after the age of 5 onwards, after which the ears will have grown into their full size.
Types of Otoplasty
An otoplasty corrects different types of deformities present in the outer ear, also known as the auricle. In general, there are three types of otoplasty, each of which aims to correct a different cosmetic concern:
Ear Pinning
Ear pinning is a technique that aims to flatten protruding ears. To perform this technique, the surgeon makes a small incision behind the ear to remove a small amount of skin and reshape or remove parts of the cartilage to create the desired shape. In some cases, the surgeon uses permanent stitches to hold the new position of the ears in place.
Our recommended surgeons also perform Earfold procedures, a less invasive option for flattening protruding ears.
Ear Augmentation
Ear augmentation is a type of otoplasty performed to increase the size of the ears. Patients born with microtia, a congenital deformity that results in small ears, are ideal candidates for this cosmetic surgery.
There are few different surgical methods that surgeons use to perform ear augmentation. Your surgeon will recommend the most appropriate surgical approach depending on your age and surgical needs. However, the surgery involves inserting either synthetic or autologous implants to enlarge the ears:
- The surgeon can shape synthetic implants according to the structure of your ear. Once fitted, the surgeon conceals the implant with a skin graft extracted from your scalp.
- An autologous implant refers to tissue taken from one area of your body and repurposed elsewhere. For ear augmentation surgery, the surgeon usually extracts cartilage from the patient’s ribs and uses it to extend the size of the ear. Over time, the new cartilage will integrate into your ear and become a natural part of the body.
Ear Reduction
Ear reduction is a type of otoplasty performed to decrease the size of the ears. Patients born with macrotia (a congenital deformity that results in abnormally large ears) or have asymmetrical ears are ideal candidates for the surgery.
Depending on the existing shape of your ear, your surgeon may reduce the upper part of the ear, the ear lobe, or both to recreate the desired shape. This cosmetic procedure involves an incision behind the ear fold through which the surgeon removes the required amount of skin and cartilage.
Otoplasty Procedure
An otoplasty procedure can be performed under local anaesthesia, sedation, or general anaesthesia and usually takes between one to three hours. The exact nature of your surgery will depend on the type of otoplasty you choose to have. In general, the surgeon makes an incision behind or inside the fold of the ear. Afterwards, the surgeon will reshape or remove skin and cartilage or add implants to the ear. Finally, the surgeon will close the incisions with sutures.
Otoplasty Recovery
Immediately after your surgery, you may experience swelling in and around the ears. You can minimise this by wearing the provided compression garment and taking any prescribed painkillers. You can expect the swelling to significantly diminish within 1-2 weeks, after which you will notice the results of your surgery and feel able to resume your daily routine. However, you will continue to see improvements up to a year after the surgery as your body continues to make a full recovery.
Otoplasty Alternatives
Ear Stitch
Ear stitch is a minimally invasive approach for correcting prominent ears. The procedure lasts just 20 minutes under local anaesthesia. After making a small incision at the back of the ear, the surgeon will use one or more of the following types of stitch techniques to correct the placement of your ears:
- The top stitch corrects ears that protrude at the top, while the rest of the ear holds a normal position. It requires a 1cm incision at the back of the ear.
- The fold stitch corrects the position of ears in which the antihelical fold ( the upper fold inside the ear) is causing the protrusion. Here, the surgeon makes a 2cm incision at the back of the ear and uses a few stitches to hold the fold in place. This technique is similar to that of the Earfold implant.
- The bowl stitch corrects ears with a disproportionately deep conchal bowl (the visible indent above the ear lobe). With a 1cm incision, the surgeon can set the conchal bowl further back to make it less prominent.
- The lobe stitch corrects ear lobes that are too prominent. Here, the surgeon places the stitch between the helix (outer rim of the ear) and the back of the conchal bowl.
Ear stitch is less invasive, has little to no downtime, and is less expensive than otoplasty or Earfold surgery. However, depending on the nature of the protrusion or other ear deformities that you wish to correct, ear stitch may not be sufficient for producing optimal results.
Earfold
Earfold is a minimally invasive cosmetic surgery that reshapes and flattens protruding ears. It involves placing a thin gold-plated curve-shaped metal implant underneath the skin of the front ear fold, thus gripping the cartilage. The surgery aims to bend the cartilage backwards and pin the ears closer to the head.
The exact placement of the Earfold varies depending on the desired results of each patient. Once the implant is inserted and correctly positioned, the antihelical fold (the curved cartilage in front of the helix) will bend into the natural and desired shape. For this procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision that is closed with dissolvable sutures.
Otoplasty vs. Earfold
While both otoplasty (ear pinning) and ear fold have the same cosmetic goal of correcting protruding ears, both surgeries have advantages and disadvantages:
- As the least complicated procedure, an Earfold is cheaper than an otoplasty.
- Unlike otoplasty, Earfold has no social downtime. However, you may experience some swelling and sensitivity in the affected area that usually dissipates within a week.
- Although otoplasty is a more invasive cosmetic surgery, it affords the surgeon greater control to manipulate the shape of the ear. Therefore, it is more likely to produce a natural result on all ear shapes.
- An ear fold can only correct protruding ears, whereas an otoplasty corrects a range of other deformities.
- Ear fold offers predictable results as your surgeon can place the implant over the ear to pre-fold it into its new position, thus demonstrating the results before the surgery.
- A cosmetic surgeon can reverse the results of an ear fold by removing the implant, whereas an otoplasty offers permanent results.
How Much Does Otoplasty Cost in the UK?
Listed below are the typical prices for otoplasty and other cosmetic ear surgeries in the UK:
| Treatment | For one ear | For two ears |
| Ear Stitch | £1,600 | £2,290 |
| Earfold | £2,500 | £3,500 |
| Otoplasty | £3,000 | £4,500 |
The exact cost of each cosmetic surgery varies depending on the type of ear surgery and the surgical complexity of your procedure. You will receive the cost of your surgery following a consultation, during which your otoplasty surgeon will examine your ears and determine the best surgical approach for reshaping and repositioning your ears.
FAQ
Does otoplasty affect hearing?
No, the surgeon performs otoplasty on the outer part of the ear. Therefore, the surgery will not affect your hearing. However, the bandages placed over your ears after surgery may temporarily impair your hearing.
Will ears relax after otoplasty?
Some patients worry that their ears may relax and revert to their original position after otoplasty. However, the risk of this happening is rare. In most cases, the ears will remain in their surgically altered state, with slight changes in position occurring over the years due to growth spurts, the cartilage in adults weakening with age, and the permanent stitches slightly loosening.
Who is the best candidate for otoplasty?
Your surgeon will determine your suitability for an otoplasty during a consultation. In general, most people over the age of 18 who wish to reshape their ears are good candidates for the surgery.
Does insurance cover otoplasty?
Otoplasty is primarily a cosmetic procedure that is usually not covered by insurance. However, your insurance may cover the cost of the surgery if you’re choosing it for functional reasons or to correct a congenital deformity.
How long do ears stay swollen after otoplasty?
The swelling in your ears after otoplasty will significantly reduce within the first week of your recovery. However, it may take up to six months for the residual swelling to completely subside.
